Light reaction of photosynthesis pdf
Photosynthesis–The Light Reactions (music video) My first video. I shot the video in the apartment we lived in in Cordoba, Argentina, in 2007. For video, I used the iSight camera on my MacBook Pro, so please forgive the video quality. It’s also a little long… In 2015, I made a series of three music videos to replace this one. Please check them out. Here’s the first. Scroll down to see
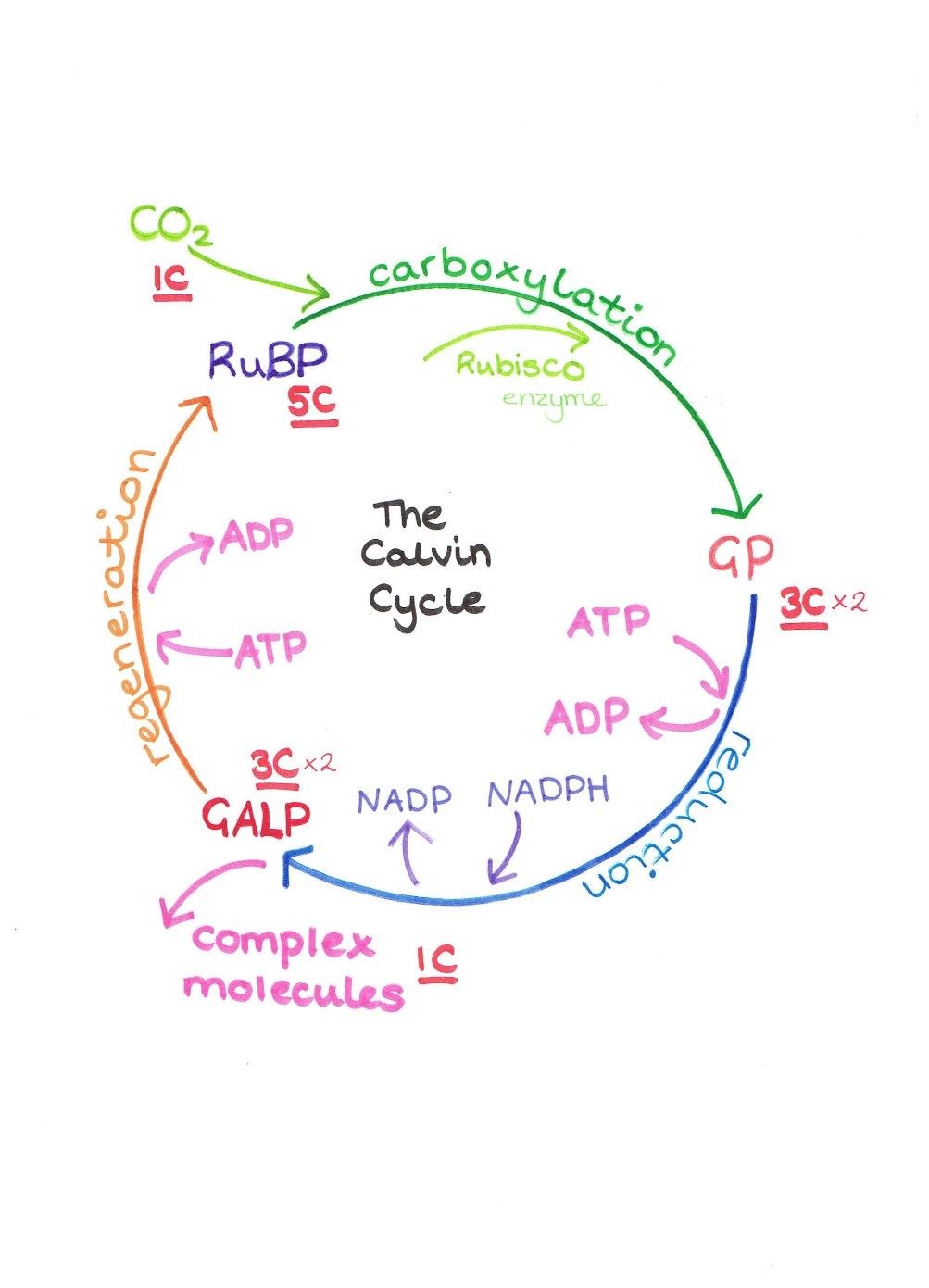
Vocabulary to know: H. Calvin cycle (Light-Independent Reactions) second stage of photosynthesis in which carbon atoms from carbon dioxide are combined, …
Photosynthesis 1 BIOLOGY 163 LABORATORY LIGHT REACTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Reviewed Fall 2018) Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of
Abstract. Historically, the role of light in photosynthesis has been ascribed either to a photolysis of carbon dioxide or to a photolysis of water and a resultant rearrangement of constituent atoms into molecules of oxygen and glucose (or formaldehyde).
that photosynthesis involves both light absorption and enzymatic reactions. Between 1883 and 1885, a German physiologist, T.W. Engelmann, in a remarkably simple experiment, demonstrated which colors of light are used in
13/04/2018 · Figure 1 Light reactions of photosynthesis and associated alternative electron transfer pathways. Linear electron flow from water to NADP + results in protons being pumped into the lumen of the thylakoid membrane, which is then used to drive the formation of ATP at the ATP synthase.
1 Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions OVERALL REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6CO2 + 6H20 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Light, Chlorophyll In reality, photosynthesis adds one CO2 at a time:
processes involved in photosynthesis, while Chapter 5 will deal with the sub-sequent chemical events involved in carbon fixation from atmospheric car-
The overall chemical reaction of photosynthesis The entire process of photosynthesis can be described by the equation: Light energy 6CO 2 + 6H 2O Æ C 6H 12O 6 + 6O 2 Chlorophyll Carbon dioxide from air is absorbed through the pores (stomata) of the leaves. Water is absorbed from the soil through the vascular system (xylem vessels) of the plant. Glucose is produced, and quickly …
Photosynthesis is a biological process by which energy contained within light is converted into chemical energy of bonds between atoms that power processes within cells.
Measuring the Hill Reaction Page 6 The Hill reaction is measured by taking a series of absorbance measurements of a sample between exposures to light (the slope of the line from the measurements yields the rate of the
Light reaction or primary photochemical reaction or hill’s reaction: The phase of reactions in photosynthesis which involves the direct sunlight is called light reaction. This reaction takes place inside the grana of chloroplast.
Under the light-dependent reactions, the light energy is converted to ATP and NADPH which are used in the second phase of photosynthesis. During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are generated by two electron transport chains, water is used and oxygen is produced.
The Process of Photosynthesis The Light Reactions

Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis USP
The various reactions in photosynthesis are spatially segregated from each other within the chloroplast. Draw a simplified diagram of a chloroplast and include these parts: outer membrane, grana, thylakoid, lumen, stroma/matrix. Refer to Figure 10.3, page 183, in Biology, 7th edition. a. Where in the chloroplast do the light In the thylakoid membranes reactions occur? b. Where in the
light reactions (also called the primary events) and dark reactions. The light reactions produce NADPH and ATP, which are then used in the dark reactions to reduce and fix carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle, the key reaction of which is catalyzed by ribulose- 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase, the most abundant protein on Earth. The cyclic tetrapyrrole pigments, called chlorophylls, play a crucial
light reactions of photosynthesis, requires light energy. The products of the light reactions are then used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Because the reactions in the second stage do not require the direct use of light energy, they are called the dark reactions of photosynthesis. In the light reactions, electrons derived from water are “excited” (raised to higher energy
Light and dark reactions in photosynthesis Photosynthesis is divided into two parts: 1. Light-dependent reactions (light reactions) 2. Light-independent reactions (dark reactions).

Exercise 4B: Photosynthesis / The Light Reaction Light is a part of a continuum of radiation or energy waves. Shorter wavelengths of energy have
Photosynthesis II-2 B. Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation In both photosystems, light drives the synthesis of ATP and NADPH by triggering a flow of electrons through the photosystem pigments and associated proteins.
5.2: The Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis. How can light be used to make food? It is easy to think of light as something that exists and allows living organisms, such as humans, to see, but light is a form of energy.
Photosynthesis (Carbon Assimilation) The light reactions result in the formation of the high-energy compounds ATP and NADPH. While these compounds can be used to drive metabolic processes, one additional critical reaction must occur: the fixation of carbon dioxide. Without CO2 fixation, the respiratory processes necessary to generate energy at night would result in an irreversible conversion
Light reaction is the first step of photosynthesis, where in the photosynthetic pigments absorbs solar radiation energy and converts it into chemical energy which is stored in ATP and NADPH molecules.
Chapter 7: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 2. The “Light” Reactions 1. Overview of Photosynthesis 3. The “Dark” Reactions . 1. Overview of Photosynthesis. What is Photosynthesis? The process of converting light energy (kinetic) into energy stored in the covalent bonds of glucose molecules (potential). • carried out by photoautotrophs • plants, phytoplankton, cyanobacteria (any photosynthetic
The process of photosynthesis has historicallybeenconsidered to consist of two parts: the light re- actions occurring in the thylakoid membrane system that produce ATP and NADPH,seeFigure1; and the light-independent carbon reactions that use ATP an d NADPH to fix atmospheric CO
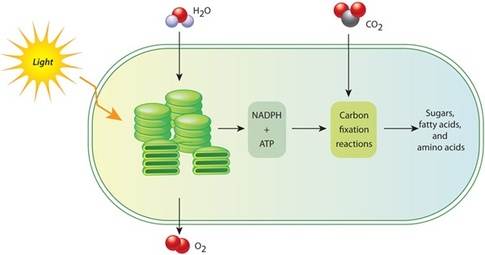
8.1 Photosynthesis converts light energy to the chemical energy of food 8.2 The light reactions convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH 8.3 The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH to reduce CO 2 to sugar The Process That Feeds the Biosphere L ife on Earth is solar powered. The chloroplasts in plants and other photosynthetic organisms capture light …
The light reaction and its products are an important step in photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process that harnesses light energy to produce carbohydrates, and is found in over 100,000 plants species on Earth. Photosynthesis is an essential process of life because the carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis are a stable form of energy that can be used by the plants themselves, or other
Light Reactions of Photosynthesis Laboratory 7. 1 Laboratory 7: Light Reactions OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Understand the cooperation between photosystems in plants through electron flow (Hill Reactions) 2. Use a redox dye to demonstrate electron flow during photosynthesis between PSI and PSII 3. Use a spectrophotometer to assess colorimetric changes …
Colonie High AP Biology DeMarco/Goldberg Chapter 10.1 –10.2 Photosynthesis: Life from Light Energy needs of life All life needs a constant input of energy
An understanding of photosynthesis is fundamental for microalgal biotechnology. The process of photosynthesis can be expressed as a light-driven redox reaction in which carbon dioxide is …
Light & Dark Reactions in Photosynthesis Wyzant Resources
Figure 1 Light reactions of photosynthesis and associated alternative electron transfer pathways. Linear electron flow from water to NADP + results in protons being pumped into the lumen of the thylakoid membrane, which is then used to drive the formation of ATP at the ATP synthase.
9-1 LABORATORY EXPLORATION The Light-dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis Plants are autotrophs, self-feeding organisms that capture light energy (photons)
In the light-dependent reaction, light energy from the sun is used to split water . which has been taken in by plants. Water, when broken, makes oxygen, hydrogen, and electrons. These
Light-Independent reactions The energy-requiring light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occurs in the stoma of the chloroplasts. A process that is “fixing” carbon atoms from CO2 to the carbon skeletons of active organic molecules uses the synthesized ATP and NADPH during the energy-releasing light-dependent reactions to supply the
1. The light-dependent reactions This (confusingly!) begins with Photosystem II, where trapped light energy is used to split water, a process known as photolysis:
Photosynthesis: Light Reactions Cyanobacteria • Overview • Structure of chloroplast • Absorption of Light • Photosystems • Electron transport chain
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists Tom Donald Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: The Role of Light The heart of photosynthesis as it occurs in most autotrophs consists of two key processes: the removal of hydrogen (H) atoms from water molecules ; the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO 2) by these hydrogen atoms to form organic molecules. The second process involves a cyclic series of reactions named (after its discoverer) the Calvin Cycle. It is discussed in
light reactions of photosynthesis , requires light energy. The products of the light reactions are The products of the light reactions are then used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
Bios 305 Prof. J. Stafstrom Topic 8. Photosynthesis page 1 8. C3 and C4 photosynthesis _____ Reading: Ch. 7 Review: overview of photosynthesis; light reactions: Calvin cycle (115-128) Photorespiration: C3, C4 and CAM pathways (127-138) Grass leaves: 566-567 – study listening tony lynch pdf 2. PHOTOSYNTHESIS: THE LIGHT REACTION AND CARBON METABOLISM The photosynthesis is the sequence of reactions, performed by green plants, blue-green
photosynthesis is essentially a light-dependent reaction in which hydrogen from a suitable oxidisable compound reduces carbon dioxide to carbohydrates. This can be expressed by: 2 2H A CO A CH O H O 2 2 2 2 Light + → + + In green plants H 2O is the hydrogen donor and is oxidised to O 2. Some organisms do not release O 2 during photosynthesis. When H 2 S, instead is the hydrogen donor for
Photosynthesis in Lichen: Light Reactions and Protective Mechanisms 151 On the other hand, non-axenic cultures can be used for studying algal metabolites or
Light Reaction is the first stage in photosynthesis where water is broken in the chlorophyll molecule into H+ ions and OH- ions in the presence of light resulting in the formation of assimilatory powers such as NADPH2 and ATP . It occurs in the grana of chloroplast.
Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis The first major set of processes in photosynthesis, in which light energy is initially converted into chemical energy as ATP and NADPH, takes place across the chloroplast thylakoid membranes, between the chloroplast stroma and the thylakoid space.
Although the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis are not affected by changes in temperature, the light independent reactions of photosynthesis are dependent on temperature. They are reactions catalysed by enzymes. As the enzymes approach their optimum temperatures the overall rate increases. It approximately doubles for every 10 °C increase in temperature. Above the optimum
Photosynthesis (Photo = light; synthesis = to join) is the single most important process on earth on which depends the existence of human beings and almost all other living organisms.
1/11/1971 · Abstract. Historically, the role of light in photosynthesis has been ascribed either to a photolysis of carbon dioxide or to a photolysis of water and a resultant rearrangement of constituent atoms into molecules of oxygen and glucose (or formaldehyde).
Light reaction is a light-dependent process which includes a series of events such as light absorption, hydrolysis, the release of oxygen, formation of ATP and NADPH. The light reaction of photosynthesis initiates only when it is supplied with light energy.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages commonly known as Light dependent Reactions and the Calvin Cycle. Light dependent Reactions Light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts and take place only when light is available.
energy of the chemical bonds (the light reactions; discussed in Sections 2.2 and 2.3). In cyanobacteria, however, the thylakoid membrane is within the cytoplasm. 2.1.3 What Can We Learn from Natural Photosynthesis to Achieve
Photosynthesis (Carbon Assimilation)
The oxygen produced in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis comes from (A) ATP (B) water (C) carbon dioxide (D) NADP+ (E) chlorophyll B H2O is split to in order to provide electrons to chlorophyll in photosystem II. A byproduct of the splitting of 2 H2O molecules is 4H
The light reactions of photosynthesis use energy from photons to generate high-energy electrons (Figure 19.2). These electrons are used directly to reduce NADP + to NADPH and are used indirectly through an electron-transport chain to generate a proton-motive force across a membrane.
For instance, photosynthesis and cellular respiration both involve a series of redox reactions (reactions involving electron transfers). In cellular respiration, electrons flow from glucose to oxygen, forming water and releasing energy. In photosynthesis, they go in the opposite direction, starting in water and winding up in glucose—an energy-requiring process powered by light. Like cellular
Summary Photosynthesis in plants uses light energy for the synthesis of carbohydrates and generation of oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. Energy stored in carbohydrates is used to power cellular processes in the plant and serves as energy resources for all forms of life. Light harvesting antenna proteins funnel energy to the reaction center. Electrons are transported through a special
LightReactions of Photosynthesis 2885 inisotonicsugar solutions (25) butinisotonic sodiumchloride (33, 35). Incomparison withthe parentleaves, washedsaline
Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis CAPP

Light-dependent reaction Simple English Wikipedia the
Oxygenic Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions (Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration) Home ; Oxygenic Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions (Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration)
C. Photochemical reactions : : Photosynthesis involves two successive steps— light reactions and dark reactions. : The light reactions take place in the grana of the chloroplasts where chlorophyll can be found located on the membranes : The dark reactions take place at the stroma of the chloroplasts where is absent from chlorophyll Light reactions (light dependent reactions) :- a) Excitation
The production of high-energy organic matter and oxygen from low-energy inorganic substances in the presence of light in plant cells, i.e. photosynthesis, satisfies the reaction equation: Read
Apago PDF Enhancer H 2O O 2 NADPH Organic molecules Stroma Photosystem Thylakoid Light-Dependent Reactions NADPNA; ATP ADP+P i Calvin Cycle CO 2 Sunlight Figure 8.2 Overview of photosynthesis.
Light and Dark Reactions in Photosynthesis Written by tutor Kathie Z. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants absorb light energy from the sun with the assistance of water and carbon dioxide, and transform it into chemical energy to make (synthesize) carbohydrate (specifically glucose) and …
pigments masks the green of the chlorophyll, but even in these leaves chlorophyll is needed for the light reactions that begin photosynthesis. In deciduous trees in the fall, leaves lose their chlorophyll so the colors of the other
Photosynthesis •Light reactions –light-dependent reactions •convert solar energy to chemical energy •ATP & NADPH •Calvin cycle –light-independent reactions
The light reactions, also known as photolysis reactions, convert energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of NADPH and ATP. These reactions must take place in the light …
Experiment 7 Photosynthesis Texas Instruments

Enhancing photosynthesis in plants the light reactions
Photosynthesis 1 Photosynthesis How do light-dependent and light-independent reactions provide food for a plant? Why? Plants are the original solar panels.
Review Article Enhancing photosynthesis in plants the


Photosynthesis 1 The Light Reactions (Ch. 8) Weebly
2.06 Intro to Photosynthesis .pdf 2.06 Intro to
– CHAPTER 2 Oxygenic Photosynthesis University Of Illinois
Photosynthesis The Light Reactions
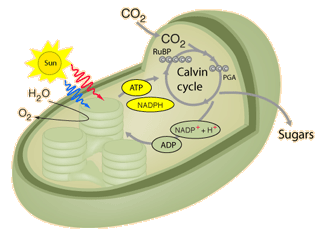
Lecture 022–Photosynthesis 1 (Light Reactions)
5.E Photosynthesis (Exercises) Biology LibreTexts
Photosynthesis University of California Davis
Lecture 022–Photosynthesis 1 (Light Reactions)
photosynthesis is essentially a light-dependent reaction in which hydrogen from a suitable oxidisable compound reduces carbon dioxide to carbohydrates. This can be expressed by: 2 2H A CO A CH O H O 2 2 2 2 Light → In green plants H 2O is the hydrogen donor and is oxidised to O 2. Some organisms do not release O 2 during photosynthesis. When H 2 S, instead is the hydrogen donor for
© 2015 American Society of Plant Biologists Tom Donald Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
The oxygen produced in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis comes from (A) ATP (B) water (C) carbon dioxide (D) NADP (E) chlorophyll B H2O is split to in order to provide electrons to chlorophyll in photosystem II. A byproduct of the splitting of 2 H2O molecules is 4H
Exercise 4B: Photosynthesis / The Light Reaction Light is a part of a continuum of radiation or energy waves. Shorter wavelengths of energy have
Photosynthesis in Lichen: Light Reactions and Protective Mechanisms 151 On the other hand, non-axenic cultures can be used for studying algal metabolites or
Photosynthesis Stages Factors And Importance Of
Photosynthesis–The Light Reactions (music video
Abstract. Historically, the role of light in photosynthesis has been ascribed either to a photolysis of carbon dioxide or to a photolysis of water and a resultant rearrangement of constituent atoms into molecules of oxygen and glucose (or formaldehyde).
The production of high-energy organic matter and oxygen from low-energy inorganic substances in the presence of light in plant cells, i.e. photosynthesis, satisfies the reaction equation: Read
Measuring the Hill Reaction Page 6 The Hill reaction is measured by taking a series of absorbance measurements of a sample between exposures to light (the slope of the line from the measurements yields the rate of the
The oxygen produced in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis comes from (A) ATP (B) water (C) carbon dioxide (D) NADP (E) chlorophyll B H2O is split to in order to provide electrons to chlorophyll in photosystem II. A byproduct of the splitting of 2 H2O molecules is 4H
1 Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions OVERALL REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6CO2 6H20 C6H12O6 6O2 Light, Chlorophyll In reality, photosynthesis adds one CO2 at a time:
Light Reaction is the first stage in photosynthesis where water is broken in the chlorophyll molecule into H ions and OH- ions in the presence of light resulting in the formation of assimilatory powers such as NADPH2 and ATP . It occurs in the grana of chloroplast.
Bios 305 Prof. J. Stafstrom Topic 8. Photosynthesis page 1 8. C3 and C4 photosynthesis _____ Reading: Ch. 7 Review: overview of photosynthesis; light reactions: Calvin cycle (115-128) Photorespiration: C3, C4 and CAM pathways (127-138) Grass leaves: 566-567
LightReactions of Photosynthesis 2885 inisotonicsugar solutions (25) butinisotonic sodiumchloride (33, 35). Incomparison withthe parentleaves, washedsaline
2. PHOTOSYNTHESIS: THE LIGHT REACTION AND CARBON METABOLISM The photosynthesis is the sequence of reactions, performed by green plants, blue-green
Light and Dark Reactions in Photosynthesis Written by tutor Kathie Z. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants absorb light energy from the sun with the assistance of water and carbon dioxide, and transform it into chemical energy to make (synthesize) carbohydrate (specifically glucose) and …
Exercise 4B: Photosynthesis / The Light Reaction Light is a part of a continuum of radiation or energy waves. Shorter wavelengths of energy have
The Light Reactions Chemistry LibreTexts
Photosynthesis Erlenbeck’s Science Room
energy of the chemical bonds (the light reactions; discussed in Sections 2.2 and 2.3). In cyanobacteria, however, the thylakoid membrane is within the cytoplasm. 2.1.3 What Can We Learn from Natural Photosynthesis to Achieve
light reactions of photosynthesis, requires light energy. The products of the light reactions are then used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water. Because the reactions in the second stage do not require the direct use of light energy, they are called the dark reactions of photosynthesis. In the light reactions, electrons derived from water are “excited” (raised to higher energy
Photosynthesis (Photo = light; synthesis = to join) is the single most important process on earth on which depends the existence of human beings and almost all other living organisms.
Light reaction is a light-dependent process which includes a series of events such as light absorption, hydrolysis, the release of oxygen, formation of ATP and NADPH. The light reaction of photosynthesis initiates only when it is supplied with light energy.
1. The light-dependent reactions This (confusingly!) begins with Photosystem II, where trapped light energy is used to split water, a process known as photolysis:
Photosynthesis 1 Photosynthesis How do light-dependent and light-independent reactions provide food for a plant? Why? Plants are the original solar panels.
pigments masks the green of the chlorophyll, but even in these leaves chlorophyll is needed for the light reactions that begin photosynthesis. In deciduous trees in the fall, leaves lose their chlorophyll so the colors of the other
Light-Independent reactions The energy-requiring light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occurs in the stoma of the chloroplasts. A process that is “fixing” carbon atoms from CO2 to the carbon skeletons of active organic molecules uses the synthesized ATP and NADPH during the energy-releasing light-dependent reactions to supply the
CHAPTER 2 Oxygenic Photosynthesis University Of Illinois
Evaluation Vernier Software & Technology
Photosynthesis (Photo = light; synthesis = to join) is the single most important process on earth on which depends the existence of human beings and almost all other living organisms.
that photosynthesis involves both light absorption and enzymatic reactions. Between 1883 and 1885, a German physiologist, T.W. Engelmann, in a remarkably simple experiment, demonstrated which colors of light are used in
1 Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions OVERALL REACTION OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS 6CO2 6H20 C6H12O6 6O2 Light, Chlorophyll In reality, photosynthesis adds one CO2 at a time:
1/11/1971 · Abstract. Historically, the role of light in photosynthesis has been ascribed either to a photolysis of carbon dioxide or to a photolysis of water and a resultant rearrangement of constituent atoms into molecules of oxygen and glucose (or formaldehyde).
Light Reactions of Photosynthesis Laboratory 7. 1 Laboratory 7: Light Reactions OBJECTIVES After completing this lab you will be able to: 1. Understand the cooperation between photosystems in plants through electron flow (Hill Reactions) 2. Use a redox dye to demonstrate electron flow during photosynthesis between PSI and PSII 3. Use a spectrophotometer to assess colorimetric changes …
The oxygen produced in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis comes from (A) ATP (B) water (C) carbon dioxide (D) NADP (E) chlorophyll B H2O is split to in order to provide electrons to chlorophyll in photosystem II. A byproduct of the splitting of 2 H2O molecules is 4H
Photosynthesis •Light reactions –light-dependent reactions •convert solar energy to chemical energy •ATP & NADPH •Calvin cycle –light-independent reactions
Photosynthesis 1 BIOLOGY 163 LABORATORY LIGHT REACTIONS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Reviewed Fall 2018) Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of
For instance, photosynthesis and cellular respiration both involve a series of redox reactions (reactions involving electron transfers). In cellular respiration, electrons flow from glucose to oxygen, forming water and releasing energy. In photosynthesis, they go in the opposite direction, starting in water and winding up in glucose—an energy-requiring process powered by light. Like cellular
9-1 LABORATORY EXPLORATION The Light-dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis Plants are autotrophs, self-feeding organisms that capture light energy (photons)
Abstract. Historically, the role of light in photosynthesis has been ascribed either to a photolysis of carbon dioxide or to a photolysis of water and a resultant rearrangement of constituent atoms into molecules of oxygen and glucose (or formaldehyde).
13/04/2018 · Figure 1 Light reactions of photosynthesis and associated alternative electron transfer pathways. Linear electron flow from water to NADP results in protons being pumped into the lumen of the thylakoid membrane, which is then used to drive the formation of ATP at the ATP synthase.
Figure 1 Light reactions of photosynthesis and associated alternative electron transfer pathways. Linear electron flow from water to NADP results in protons being pumped into the lumen of the thylakoid membrane, which is then used to drive the formation of ATP at the ATP synthase.
Bios 305 Prof. J. Stafstrom Topic 8. Photosynthesis page 1 8. C3 and C4 photosynthesis _____ Reading: Ch. 7 Review: overview of photosynthesis; light reactions: Calvin cycle (115-128) Photorespiration: C3, C4 and CAM pathways (127-138) Grass leaves: 566-567
1 comment so far